- Forum
- categories
- Sanitation systems
- Faecal sludge management (FSM)
- Pit or vault content research, accumulation rates and faecal sludge characteristics
- Reply: Methods for Fecal Sludge Analysis book (now available, free pdf file)
Reply: Methods for Fecal Sludge Analysis book (now available, free pdf file)
13.6k views
- AjitSeshadri
-

- Marine Chief Engineer by profession (1971- present) and at present Faculty in Marine Engg. Deptt. Vels University, Chennai, India. Also proficient in giving Environmental solutions , Designation- Prof. Ajit Seshadri, Head- Environment, The Vigyan Vijay Foundation, NGO, New Delhi, INDIA , Consultant located at present at Chennai, India
Re: Reply: Methods for Fecal Sludge Analysis book (now available, free pdf file)
We appreciate your gesture on making a Book available on FSM Methods.
Also given in smaller sizes, chapter wise, very thoughtful.
All need to follow this principle.
Well wishes and thanks
Prof Ajit Seshadri
Head-Environment , VigyanVijay Foundation, Consultant (Water shed Mngmnt, WWT, WASH, others)Located at present at Chennai, India
Please Log in to join the conversation.
You need to login to replyRe: Reply: Methods for Fecal Sludge Analysis book (now available, free pdf file)
If you are having problems with downloading the book, we also put a lower resolution version here that you can download by individual chapter
www.sandec.ch/fsm_methods
Best regards,
Linda
Group Leader MEWS - Management of Excreta, Wastewater, and Sludge
Eawag - Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science & Technology
Sandec - Department of Water & Sanitation in Developing Countries
www.sandec.ch/fsm_tools
www.eawag.ch
Please Log in to join the conversation.
You need to login to reply- Elisabeth
-
- User is blocked
- Freelance consultant since 2012
Less- Posts: 3372
- Karma: 54
- Likes received: 932
Re: Reply: Methods for Fecal Sludge Analysis book (now available, free pdf file)
Open Access ebook
Access ebook
This takes you to this page: iwaponline.com/ebooks/book/823/Methods-f...ecal-Sludge-Analysis
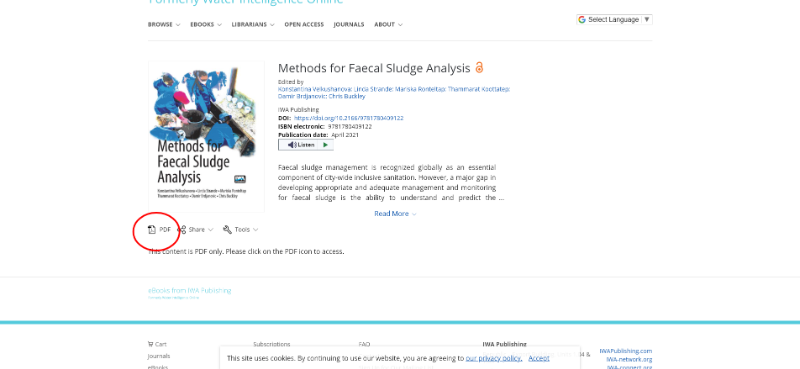
Here you need to click on the pdf icon. So they are making it a bit hard but it's there!
I've also attached a screenshot. You need to click on the pdf icon in the yellow circle on this page . It's 90 MB large, so it will take a while to download.
Regards,
Elisabeth
Freelance consultant on environmental and climate projects
Attachments:
Please Log in to join the conversation.
You need to login to reply- Wawa
-
- User
Less- Likes received: 0
- Elisabeth
-
- User is blocked
- Freelance consultant since 2012
Less- Posts: 3372
- Karma: 54
- Likes received: 932
Re: Methods for Fecal Sludge Analysis book (now available, free pdf file)
Take a look: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fecal_sludge_management
As a result, the book is now cited 12 times in the Wikipedia article.
More work is yet to be done to update the content about treatment options in particular.
Anyone with an interest in FSM and an interest in educating the public is welcome to help with this Wikipedia editing work. It's so easy now, you can just copy from the book and cite the source (just make sure the language is understandable for lay persons).
Here on the talk page Linda has also mentioned some further things that need improvement:
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Talk:Fecal_sludge_...improve_this_article
Regards,
Elisabeth
Freelance consultant on environmental and climate projects
Please Log in to join the conversation.
You need to login to reply- Elisabeth
-
- User is blocked
- Freelance consultant since 2012
Less- Posts: 3372
- Karma: 54
- Likes received: 932
Re: Sludge Analysis Book (now available, free pdf file)
I am so happy because they have published it not just as a free pdf file but, even better, with an open access licence!
Here is the link to the book: www.iwapublishing.com/books/978178040911...ecal-sludge-analysis
Here is the information about the licence:
The pdf file is quite big (90 MB), so if your internet connection is slow you might need to be patient.This is an Open Access book distributed under the terms of the Creative CommonsAttribution Licence (CC BY 4.0), which permits copying and redistribution provided
the original work is properly cited.
(creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). This does not affect the rights
licensed or assigned from any third party in this book.
This title was made available Open Access through a
partnership with Knowledge Unlatched.
IWA Publishing would like to thank all of the libraries for
pledging to support the transition of this title to Open Access
through the 2020 KU Partner Package program.
I like the image they have used for their cover, very well done:
The table of content is copied below. Happy reading!
And I look forward to working with Linda (and anyone else who's keen) to use this book to update the Wikipedia article about FSM.
Elisabeth
+++++++
Table of contents
1.1 City-wide inclusive sanitation 2
1.2 What is faecal sludge? 3
1.3 Towards standardisation of methods for faecal sludge analysis 6
1.4 Integrated approach to data collection 7
1.5 Additional resources 9
2. FAECAL SLUDGE PROPERTIES AND CONSIDERATIONS FOR CHARACTERISATION 15
2.1 Introduction 16
2.2 Types of faecal sludge 16
2.3 Factors influencing the faecal sludge characteristics along the sanitation service chain 18
2.3.1 Inputs to faecal sludge production 19
2.3.1.1 Excreta 19
2.3.1.2 Water inputs 19
2.3.1.3 Annal cleansing materials 21
2.3.1.4 Additional inputs 21
2.3.2 Factors affecting characteristics of accumulated faecal sludge 21
2.3.2.1 Technical factors 22
2.3.2.2 Demographic factors 22
2.3.2.3 Environmental factors 23
2.3.2.4 Variability of accumulated faecal sludge 23
2.3.2.5 Developments and innovations in onsite containment 24
2.3.3 Emptying and transport 26
2.3.3.1 Storage time or emptying frequency 26
2.3.3.2 Manual or mechanical emptying 27
2.3.3.3 Transportation 27
2.3.3.4 Innovations in faecal sludge emptying and transportation 27
2.3.4 Treatment and end use 28
2.3.4.1 Faecal sludge treatment plants 28
2.3.4.2 End use or disposal 30
2.3.4.3 Innovations in treatment and end use 30
2.3.4.4 Container-based sanitation (CBS) 31
2.3.4.5 Summary of technologies along the sanitation service chain 31
2.4 Properties of faecal sludge and selecting methods of characterisation 34
2.4.1 Faecal sludge properties 35
2.4.1.1 Chemical and physico-chemical properties 35
2.4.1.2 Physical properties 37
2.4.1.3 Biological properties 37
2.4.2 Selection of appropriate methods for characterisation 38
2.5 Setting up laboratories for faecal sludge analysis 39
2.5.1 Faecal sludge laboratory workflow 40
2.5.2 Health and safety practices 41
2.5.3 Laboratory management systems 41
2.5.4 Case studies of global faecal sludge laboratories 43
2.5.5 Global Partnership of Laboratories for Faecal Sludge Analysis (GPLFSA) 48
2.6 Outlook 48
3. FAECAL SLUDGE SAMPLE COLLECTION AND HANDLING 55
3.1 Introduction 56
3.2 Sampling objective 56
3.2.1 Containment 56
3.2.2 Collection and transport 57
3.2.3 Treatment 57
3.2.4 End use 57
3.3 Representativeness 58
3.4 Sampling techniques 58
3.4.1 Grab sampling 58
3.4.2 Composite sampling 59
3.5 Sampling and measuring devices 60
3.5.1 L-stick sludge and scum measuring device 62
3.5.2 Core sampling device 62
3.5.3 Vacuum sludge sampling device 63
3.5.4 Cone-shaped sampling device 64
3.5.5 Grab sampling device - horizontal 65
3.5.6 Grab sampling device - vertical 65
3.5.7 Automatic composite sampler 66
3.5.8 Distance laser measuring device 66
3.5.9 Portable penetrometer 67
3.6 Sampling methods and location 68
3.6.1 Sampling in situ from onsite containment technologies 68
3.6.2 Sampling during emptying of onsite containment technologies 71
3.6.3 Sampling at faecal sludge treatment plants 76
3.7 Sample size
3.8 Health and safety
3.9 Sample collection
3.10 Recording of sample collection
3.11 Transport
3.12 Storage and preservation
3.13 Example of sampling kit
3.14 Outlook 83
4. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN FOR THE DEVELOPMENT, TRANSFER, SCALING‐UP, AND
OPTIMISATION OF TREATMENT TECHNOLOGIES: CASE STUDIES OF DEWATERING
AND DRYING 85
4.1 Introduction 86
4.2 Experimentation in faecal sludge management 87
4.2.1 Scales of experiments 87
4.2.2 Designing an experiment 88
4.3 Transferring technology: conditioning to improve dewatering 89
4.3.1 Introduction to faecal sludge dewatering with conditioners 89
4.3.2 Types and mechanisms of conditioners 90
4.3.3 Key parameters for selection of conditioners and optimal dose 91
4.3.4 Laboratory- and pilot-scale testing 91
4.3.5 Case studies - conditioning for improved dewatering 92
4.4 Transferring technology: thermal drying for resource recovery of dried sludge for energy 98
4.4.1 Introduction to resource recovery of faecal sludge as solid fuel 98
4.4.2 Introduction to faecal sludge drying 98
4.4.3 Types and mechanisms of thermal drying (technical background) 99
4.4.4 Key parameters when implementing thermal-drying technologies
4.4.5 Laboratory-scale and pilot-scale testing
4.4.6 Case studies - thermal drying for energy recovery
5. ESTIMATING QUANTITIES AND QUALITIES (Q&Q) OF FAECAL SLUDGE AT
COMMUNITY TO CITY‐WIDE SCALES 115
5.1. Introduction 116
5.2 Background 117
5.2.1 Scenario projections for planning and management 117
5.2.2 Mass balance: quantifying loadings of faecal sludge 119
5.2.2.1 Production of excreta and faecal sludge 120
5.2.2.2 Accumulation of faecal sludge 120
5.2.2.3 Fate of faecal sludge 122
5.3 Steps for implementation 122
5.4 Further research and analytical possibilities 136
5.4.1 Remote sensing 136
5.4.2 Additional spatial analysis 136
5.4.3 Interrelationships between sludge characteristics 136
5.4.4 Evaluating categories of data to evaluate separately 138
5.4.5 Predictive models 139
5.4.6 Sensitivity analysis and error propagation 139
5.5 Outlook 141
4.5 Transferring technology: microwave drying for resource recovery of dried sludge for energy
4.6 Outlook
6. TOWARDS CITY‐WIDE INCLUSIVE SANITATION (CWIS) MODELLING: MODELLING
OF FAECAL SLUDGE CONTAINMENT/TREATMENT PROCESSES 145
6.1 Background 146
6.2 Introduction to modelling - learning from activated sludge models 148
6.2.1 What is a model? 148
6.2.2 Modelling basics 151
6.2.2.1 Model building 151
6.2.2.2 General activated sludge model set‐up 152
6.2.2.3 The matrix notation 154
6.2.2.4 Wastewater treatment models 155
6.2.2.5 Modelling protocols 156
6.3 Towards an onsite sanitation modelling framework 160
6.3.1 Onsite sanitation modelling: formulation of objectives 160
6.3.2 Onsite sanitation modelling: process description 160
6.3.2.1 Portable toilets 161
6.3.2.2 Single pit latrines 162
6.3.2.3 Septic tanks 164
6.3.3 Onsite sanitation modelling: data collection and verification 168
6.3.4 Onsite sanitation modelling: model structure 171
6.3.4.1 Model structure of commonly used onsite sanitation systems 171
6.3.4.2 Model structures of other sanitation systems 174
6.3.5 Onsite sanitation modelling: characterisation of flows
6.3.6 Onsite sanitation modelling: calibration and validation
6.3.7 Onsite sanitation modelling: detailed characterisation 177
6.3.7.1 Faecal sludge characterisation and fractionation 177
6.3.7.2 Inhibition and toxicity 179
6.3.7.3 Pathogen inactivation 180
6.3.8 Modelling applications, benefits and challenges 184
6.4 Outlook 185
7. FAECAL SLUDGE SIMULANTS: REVIEW OF SYNTHETIC HUMAN FAECES AND
FAECAL SLUDGE FOR SANITATION AND WASTEWATER RESEARCH 195
7.1 Introduction 196
7.2 Characteristics of faeces and faecal sludge 197
7.2.1 Faeces 197
7.2.2 Faecal sludge 198
7.3 Synthetic faeces and faecal sludge found in literature 204
7.3.1 Physical parameters 204
7.3.1.1 Faeces simulants 204
7.3.1.2 Faecal sludge simulants 206
7.3.2 Chemical, biological, and thermal parameters 207
7.3.2.1 Faeces simulants 207
7.3.2.2 Faecal sludge simulants 209
7.4 Discussion 211
7.4.1 Development of new simulants 214
7.4.1.1 Synthetic faeces 214
7.4.1.2 Synthetic faecal sludge 216
7.5 Conclusions 216
8. LABORATORY PROCEDURES AND METHODS FOR CHARACTERISATION OF
FAECAL SLUDGE 235
8.1 Introduction 236
8.2 Health and safety (H&S) 238
8.2.1 Monitoring and responsibilities 238
8.2.2 Standard operating procedures (SOPs) 239
8.2.3 Handling of faecal sludge 241
8.2.3.1 Personal protective equipment 241
8.2.3.2 Vaccinations / inoculations 242
8.2.3.3 ‘Clean’ and ‘dirty’ work areas 242
8.2.3.4 Sampling 242
8.3 Quality assurance and quality Control (QA/QC) 242
8.3.1 Training 243
8.3.2 Standard operating procedures 243
8.3.3 Laboratory facilities 243
8.3.4 Sample chain of command 244
8.3.4.1 Laboratory photographs and notebooks 244
8.3.4.2 Equipment maintenance and calibration 245
8.3.4.3 Reporting of results 246
8.3.4.4 Checking compliance 246
8.3.5 Quality control 247
8.4 Selection of the appropriate method for the purpose of characterisation 249
8.4.1 Faecal sludge storage and preservation 251
8.4.2 Faecal sludge sample preparation for analysis 251
8.2.4.1 Homogenisation of samples 252
8.2.4.2 Dilution of samples 252
8.2.4.3 Filtration 253
8.2.4.4 Centrifugation 253
8.4.3 Sample and chemical disposal 253
8.5 Shipping and receiving of faecal sludge samples and equipment 254
8.6 Chemical and physico-chemical properties 257
8.6.1 Solids and moisture content 257
8.6.1.1 Total solids and moisture content -
volumetric and gravimetric methods by oven drying 257
8.6.1.2 Volatile and fixed solids - ignition method 260
8.6.1.3 Total suspended solids and total dissolved solids - oven drying method 263
8.6.1.4 Volatile suspended solids - ignition method 266
8.6.1.5 Total solids and moisture content - thermal balance (moisture analyser) method 268
8.6.1.6 Sand content 269
8.6.2 Chemical oxygen demand (COD) 271
8.6.2.1 Chemical oxygen demand - closed reflux spectrophotometric method 271
8.6.2.2 Chemical oxygen demand - closed reflux titrimetric method 274
8.6.3 Fat and fibre 278
8.6.3.1 Crude fat - Soxhlet extraction method 278
8.6.3.2 Crude fibre - filtration method 282
8.6.4 Nitrogen 286
8.6.4.1 Total nitrogen - spectrophotometric method 287
8.6.4.2 Ammonium - colorimetric (test strip) method 290
8.6.4.3 Ammonium - phenate spectrophotometric method 292
8.6.4.4 Ammonia - distillation and titration method 295
8.6.4.5 Nitrite - colorimetric (test strip method) 299
8.6.4.6 Nitrite - spectrophotometric method 301
8.6.4.7 Nitrate - colorimetric (test strip method) 303
8.6.4.8 Nitrate - cadmium reduction spectrophotometric method 305
8.6.4.9 Total Kjeldahl nitrogen - distillation and titration method 308
8.6.5 Phosphorus 312
8.6.5.1 Total phosphorus and orthophosphate - spectrophotometric method 312
8.6.5.2 Orthophosphate - colorimetric (test strip) method 316
8.6.6 pH and electrical conductivity 318
8.6.6.1 pH - electrode method 319
8.6.6.2 Electrical conductivity - electrode method 322
8.6.7 Elemental analysis 324
8.6.7.1 Metals - overview 324
8.6.7.2 Metals - acid digestion for environmentally available metals 325
8.6.7.3 Ultimate analysis - total carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and sulphur 328
8.6.7.4 Chlorine - colorimetric (test strip) method 331
8.6.7.5 Chlorine - spectrophotometric method 332
8.6.7.6 Chloride - colorimetric (test strip) method 334
8.6.7.7 Chloride - spectrophotometric method 336
8.6.8 Colour and turbidity 338
8.6.8.1 Colour - visual comparison method 339
8.6.8.2 Turbidity - nephelometric method 341
8.6.9 Settleability and dewaterability 344
8.6.9.1 Jar test 344
8.6.9.2 Capillary suction time 346
8.6.9.3 Water activity 348
8.6.9.4 Sludge volume index 351
8.7 Physical properties 352
8.7.1 Physical and mechanical properties 352
8.7.1.1 Density - mass and volume measurement method 353
8.7.1.2 Density - volume displacement method 354
8.7.1.3 Particle size - laser light scattering method 356
8.7.1.4 Rheological properties - rheometer method 360
8.7.1.5 Liquid limit - cone penetrometer method 362
8.7.1.6 Plastic limit - thread-rolling method 364
8.7.1.7 Compressibility and stickiness - texture analyser method 366
8.7.2 Physical and thermal properties 368
8.7.2.1 Thermal conductivity - thermal conductivity analyser method 368
8.7.2.2 Calorific value - bomb calorimeter method 370
8.8 Biological properties 373
8.8.1 Pathogens 373
8.8.1.1 E. coli and total coliforms - colony forming unit method 374
8.8.1.2 E. coli, faecal coliforms, and total coliforms - the most probable number method 378
8.8.1.3 Bacteriophage - plaque assay method 383
8.8.1.4 Helminth - microscopy method 386
Freelance consultant on environmental and climate projects
Attachments:
Please Log in to join the conversation.
You need to login to reply- Elisabeth
-
- User is blocked
- Freelance consultant since 2012
Less- Posts: 3372
- Karma: 54
- Likes received: 932
Re: Methods for Fecal Sludge Analysis Book (to be published 15 April 2021)
Methods for Faecal Sludge Analysis
www.iwapublishing.com/books/978178040911...ecal-sludge-analysis
Editor(s):OVERVIEW
The importance and need for faecal sludge management has been recognised worldwide. One major gap in developing appropriate and adequate faecal sludge treatment and monitoring techniques is the ability to understand faecal sludge characteristics, its quantification and correlation to source populations. Faecal sludge characteristics are highly variable, but as standard methods for sampling and analysis do not exist, results are not comparable and hence the actual variability is not yet fully understood.
Due to the lack of standard methods for sampling and analysis of faecal sludge, standard methods from other fields such as water, wastewater and soil science are usually applied. However, these methods are not necessarily the most suitable for faecal sludge, and have not been specifically adapted for that purpose. Characteristics of faecal sludge are typically different from these other matrices by orders of magnitude. The methods for faecal sludge sampling are also greatly complicated by the wide range of technologies in each local context, and the heterogeneity within systems. Another gap in existing knowledge is how to quantify faecal sludge on a city-wide scale, or scale relevant for the design of treatment technologies. Moreover, the lack of standardisation complicates the transfer of knowledge and data between different regions and institutions as the results are not comparable. This illustrates the urgent need to establish common methods and procedures for faecal sludge characterisation and quantification.
This book aims to address these challenges and provide a basis towards standardized methods for characterisation and quantification of faecal sludge from onsite sanitation technologies, including sampling techniques and health and safety procedures for faecal sludge handling. It also aims at improved communication between sanitation practitioners, comparative faecal sludge database and improved confidence in the methods and obtained results. The book will be beneficial for researchers, laboratory technicians, academics, students and sanitation practitioners.
Konstantina Velkushanova
Linda Strande
Mariska Ronteltap
Thammarat Koottatep
Damir Brdjanovic
Chris Buckley
Looking forward to it (hoping the electronic version won't be behind a paywall).
Elisabeth
Freelance consultant on environmental and climate projects
Please Log in to join the conversation.
You need to login to reply- Nida
-
 Topic Author
Topic Author- PhD Scholar working on Fecal sludge treatment in Pakistan
Less- Posts: 25
- Likes received: 6
I searched a bit for the ebook ISBN and it seems like the ebook isn't available yet and will be released only on 15th of January 2021.
Edit: Here is a link to a recent presentation: (starts at 1:06) mentioning it will be available by the "end of 2020".
Please Log in to join the conversation.
You need to login to reply- Nida
-
 Topic Author
Topic Author- PhD Scholar working on Fecal sludge treatment in Pakistan
Less- Posts: 25
- Likes received: 6
Can anyone kindly send me ebook "Methods for Fecal Sludge analysis"
Although it says its open access but i am unable to download.
Please help.
Regards,
Please Log in to join the conversation.
You need to login to reply- Forum
- categories
- Sanitation systems
- Faecal sludge management (FSM)
- Pit or vault content research, accumulation rates and faecal sludge characteristics
- Reply: Methods for Fecal Sludge Analysis book (now available, free pdf file)